Terbutaline Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Terbutaline
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (ter byoo' ta leen)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Terbutaline is used to prevent and treat wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness caused by asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Terbutaline is in a class of medications called beta agonists. It works by relaxing and opening the airways, making it easier to breathe.
How should this medicine be used?
Terbutaline comes as a tablet to take by mouth. The tablets are usually taken three times a day, once every six hours. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take terbutaline exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Each dose of terbutaline should control your symptoms for at least 6 hours after you take it. If you find that your symptoms return before it is time for your next dose, that terbutaline does not control your symptoms as well as it did at the beginning of your treatment, or that your symptoms are getting worse, call your doctor. These may be signs that your condition is worsening.
Terbutaline may control your symptoms but will not cure your condition. Continue to use terbutaline even if you feel well. Do not stop taking terbutaline without talking to your doctor.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking terbutaline,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to terbutaline, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in terbutaline tablets. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: beta blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), carteolol (Cartrol), labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate), metoprolol (Lopressor), nadolol (Corgard), propanolol (Inderal), sotalol (Betapace), and timolol (Blocadren); certain diuretics ( 'water pills'); other medications for asthma; and medications for colds, appetite control, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Also tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medications or if you have stopped taking them in the past 2 weeks: tricyclic antidepressants including amitriptyline, amoxapine, clomipramine (Anafranil), desipramine (Norpramin), doxepin, imipramine (Tofranil), maprotiline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), protriptyline (Vivactil), and trimipramine (Surmontil) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) including isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam, Zelapar), and tranylcypromine (Parnate). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had an irregular heartbeat, heart disease, high blood pressure, an overactive thyroid gland, diabetes, or seizures.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking terbutaline, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking terbutaline.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Terbutaline may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- uncontrollable shaking of a part of the body
- nervousness
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- weakness
- headache
- nausea
- sweating
- dry mouth
- increased difficulty breathing
- tightening of the throat
- fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
- chest pain
- seizures
Terbutaline may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while you are taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Sympathomimetics
- Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists
- Bronchodilator Agents
- Tocolytic Agents
- Respiratory System
- Drugs for Obstructive Airway Diseases
- Selective Beta-2-Adrenoreceptor Agonists
- Adrenergics, Inhalants
- Adrenergics for Systemic Use
- Beta2 Agonists
- Selective beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonists
| Prescribed | For the prevention and reversal of bronchospasm in patients 12 years of age and older with reversible, obstructive airway disease, as well as sympt... |
| Weight : | 225.2842 |
| Structure | Terbutaline |
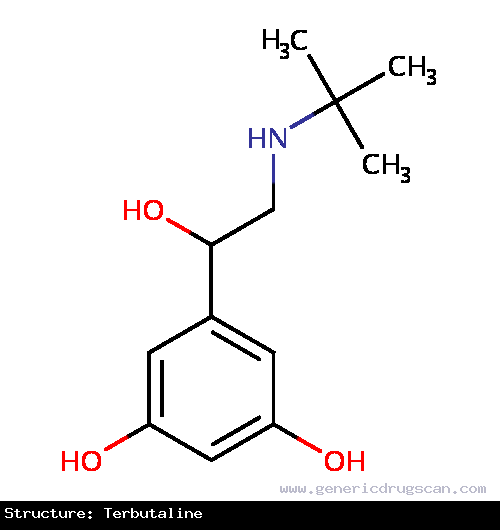 | |
| Formula | C12H19NO3 |
Terbutaline has 2 Brands listed
| Bricanyl (2.5 mg) | Bricanyl Misthaler (250 mcg) |
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
