Pyridoxine Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Pyridoxine
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (peer i dox' een)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Pyridoxine, vitamin B6, is required by your body for utilization of energy in the foods you eat, production of red blood cells, and proper functioning of nerves. It is used to treat and prevent vitamin B6 deficiency resulting from poor diet, certain medications, and some medical conditions.
This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should this medicine be used?
Pyridoxine comes in regular and extended-release (long-acting) tablets. It usually is taken once a day. Follow the directions on your prescription label or package label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take pyridoxine exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Do not chew, crush, or cut extended-release tablets; swallow them whole.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking pyridoxine,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to pyridoxine or any other drugs.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications you are taking, especially levodopa (Larodopa, Sinemet), phenobarbital, phenytoin (Dilantin), and other vitamins.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking pyridoxine, call your doctor.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Pyridoxine may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- upset stomach
- headache
- sleepiness
- tingling, prickling, burning, or sensation of tightness of the hands and feet
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Vitamin B Complex
- Vitamins
- Alimentary Tract and Metabolism
- Other plain vitamin preparations
| Prescribed | For the treatment of vitamin B6 deficiency and for the prophylaxis of isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy. |
| Weight : | 169.1778 |
| Structure | Pyridoxine |
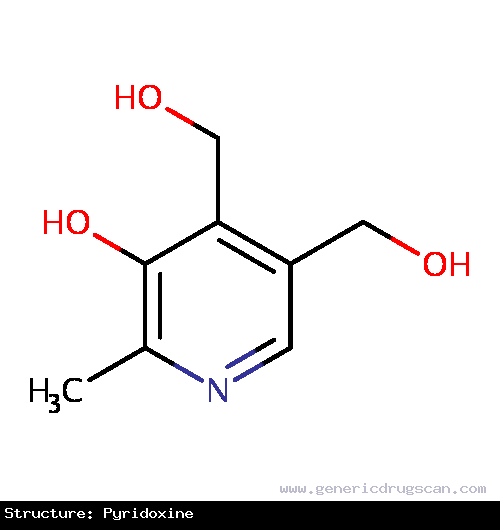 | |
| Formula | C8H11NO3 |
Pyridoxine has 9 Brands listed
| B Long (100 mg) | B Six (100 mg) |
| Ingavit B6 (10 mg) | Ingavit B6 (50 mg) |
| Mecoba Alfa (3 mg) | Nucetam (100 mg) (Pyridoxine) |
| Perivin (50 mg) | Pyricontin (100 mg) |
| Pyridox (50 mg) |
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
