Phenytoin Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Phenytoin
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (fen' i toyn)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Phenytoin is used to control certain type of seizures, and to treat and prevent seizures that may begin during or after surgery to the brain or nervous system. Phenytoin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. It works by decreasing abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
How should this medicine be used?
Phenytoin comes as an extended-release (long-acting) capsule, a chewable tablet, and a suspension (liquid) to take by mouth. The chewable tablet and suspension are usually taken two or three times a day. The extended-release capsules are usually taken 1 to 4 times a day. Take phenytoin at around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take phenytoin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor will start you on a low dose of phenytoin and gradually increase your dose, not more often than once every 7 to 10 days.
Different phenytoin products are absorbed by the body in different ways and cannot be substituted for one another. If you need to switch from one phenytoin product to another, your doctor may need to adjust your dose. Each time you receive your medication, check to be sure that you have received the phenytoin product that was prescribed for you. Ask your pharmacist if you have are not sure that you received the right medication.
Shake the liquid well before each use to mix the medication evenly. Use an accurate measuring device to be sure you receive the correct amount of medication. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about how to measure your dose.
Swallow the extended-release capsules whole; do not split, chew, or crush them. Do not take capsules that are discolored.
You may chew the chewable tablets thoroughly before swallowing them, or you may swallow them whole without chewing.
If you are receiving formula or supplements through a feeding tube, talk to your doctor about when you should take phenytoin. You will need to allow some time between receiving your feedings and taking phenytoin.
Phenytoin may help control your condition but will not cure it. Continue to take phenytoin even if you feel well. Do not stop taking phenytoin without talking to your doctor, even if you experience side effects such as unusual changes in behavior or mood. If you suddenly stop taking phenytoin, your seizures may worsen. Your doctor will probably decrease your dose gradually.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking phenytoin,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to phenytoin, other hydantoin medications such as ethotoin (Peganone) or fosphenytoin (Cerebyx), or any other medications. Also tell your doctor if you are allergic to carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Equetro, Tegretol), or if your doctor chose not to treat you with carbamazepine because laboratory testing showed that you have an inherited risk factor that makes it more likely that you will have an allergic reaction to carbamazepine. This risk factor may also increase the chance that you will have an allergic reaction to phenytoin.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone); anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin (Coumadin); certain other antidepressants including amitriptyline (Elavil), amoxapine, clomipramine (Anafranil), desipramine (Norpramin), doxepin (Sinequan), imipramine (Tofranil), maprotiline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), protriptyline (Vivactil), and trimipramine (Surmontil); chloramphenicol; chlordiazepoxide (Librium, in Limbitrol); diazepam (Valium); digoxin (Lanoxin); disulfiram (Antabuse); doxycycline (Doryx, Monodox,Vibramycin, others); fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem, in Symbyax); furosemide (Lasix); H2 antagonists such as cimetidine (Tagamet), famotidine (Pepcid), nizatidine (Axid), and ranitidine (Zantac); hormonal contraceptives (birth control pills, patches, rings, or injections); hormone replacement therapy (HRT); isoniazid (in Rifamate, in Rifater); medications for mental illness and nausea; other medications for seizures such as carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Equetro, Tegretol), ethosuximide (Zarontin), methsuximide (Celontin), phenobarbital, and valproic acid (Depakon, Depakene, Stavzor); methylphenidate (Daytrana, Concerta, Metadate, Ritalin); molindone (Moban); oral steroids such as dexamethasone (Decadron, Dexone), methylprednisolone (Medrol), prednisolone, and prednisone (Deltasone); paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva); quinidine; reserpine (Serpalan); rifampin (Rimactane, in Rifamate, in Rifater); salicylate pain relievers such as aspirin, choline magnesium trisalicylate, choline salicylate (Arthropan), diflunisal (Dolobid), magnesium salicylate (Doan's, others), and salsalate (Argesic, Disalcid, Salgesic); sucralfate (Carafate); sulfa antibiotics; theophylline (Theo-Dur); ticlopidine (Ticlid); tolbutamide; trazodone; and vitamin D. Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you more carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you are taking antacids that contain calcium (Maalox, Mylanta, Tums, others). Your doctor may tell you to allow some time to pass between taking the antacid and taking phenytoin.
- tell your doctor if you drink or have ever drunk large amounts of alcohol and if you have or have ever had diabetes, porphyria (condition in which cerain natural substances build up in the body and may cause stomach pain, changes in thinking or behavior, or other symptoms), or kidney or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking phenytoin, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking phenytoin.
- you should know that this medication may cause dizziness and problems with coordination. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this medication affects you.
- talk to your doctor about the safe use of alcohol while you are taking this medication.
- you should know that your mental health may change in unexpected ways and you may become suicidal (thinking about harming or killing yourself or planning or trying to do so) while you are taking phenytoin. A small number of adults and children 5 years of age and older (about 1 in 500 people) who took anticonvulsants such as phenytoin to treat various conditions during clinical studies became suicidal during their treatment. Some of these people developed suicidal thoughts and behavior as early as one week after they started taking the medication. There is a risk that you may experience changes in your mental health if you take an anticonvulsant medication such as phenytoin, but there may also be a risk that you will experience changes in your mental health if your condition is not treated. You and your doctor will decide whether the risks of taking an anticonvulsant medication are greater than the risks of not taking the medication. You, your family, or your caregiver should call your doctor right away if you experience any of the following symptoms: panic attacks; agitation or restlessness; new or worsening irritability, anxiety, or depression; acting on dangerous impulses; difficulty falling or staying asleep; aggressive, angry, or violent behavior; mania (frenzied, abnormally excited mood); talking or thinking about wanting to hurt yourself or to end your life; withdrawing from friends and family; preoccupation with death and dying; giving away prized possessions; or any other unusual changes in behavior or mood. Be sure that your family or caregiver knows which symptoms may be serious so they can call the doctor if you are unable to seek treatment on your own.
- talk to your doctor about the best way to care for your teeth, gums, and mouth during your treatment with phenytoin. It is very important that you care for your mouth properly to decrease the risk of gum damage caused by phenytoin.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Phenytoin may cause an increase in your blood sugar. Talk to your doctor about the symptoms of high blood sugar and what to do if you experience these symptoms.Phenytoin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- uncontrollable eye movements
- abnormal body movements
- loss of coordination
- confusion
- slowed thinking
- slurred speech
- dizziness
- headache
- nausea
- vomiting
- constipation
- unwanted hair growth
- coarsening of facial features
- enlargement of lips
- overgrowth of gums
- pain or curving of the penis
- swollen glands
- fever
- blisters
- rash
- joint pain
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- pain in the upper right part of the stomach
- excessive tiredness
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- loss of appetite
- flu-like symptoms
Phenytoin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while you are taking this medication.
Taking phenytoin may increase the risk that you will develop osteomalacia (weakening and softening of the bones) and problems with your lymph nodes including Hodgkin's disease (cancer that begins in the lymph system). Talk to your doctor about the risks of using this medication to treat your condition.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature, away from light and excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Do not freeze the liquid. Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blockers
- Hydantoin Derivatives
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2B6 Inhibitors
- CYP2B6 Inhibitors (strong)
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2B6 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C19 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inducers
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Anticonvulsants
- Antiepileptics
| Prescribed | For the control of generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal) and complex partial (psychomotor, temporal lobe) seizures and prevention and treatment of s... |
| Weight : | 252.268 |
| Structure | Phenytoin |
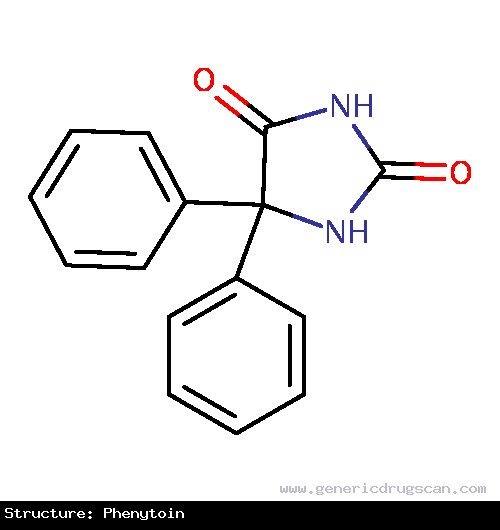 | |
| Formula | C15H12N2O2 |
Phenytoin has 29 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
