Indinavir Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Indinavir
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (in din' a veer)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Indinavir is used along with other medications to treat human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Indinavir is in a class of medications called protease inhibitors. It works by decreasing the amount of HIV in the blood. Although indinavir does not cure HIV, it may decrease your chance of developing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and HIV-related illnesses such as serious infections or cancer. Taking these medications along with practicing safer sex and making other life-style changes may decrease the risk of transmitting the HIV virus to other people.
How should this medicine be used?
Indinavir comes as a capsule to take by mouth. It is usually taken every 8 hours (three times a day). Take indinavir at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take indinavir exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Take indinavir on an empty stomach, 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after meals, with water, skim or nonfat milk, juice, coffee, or tea. However, if indinavir upsets your stomach, it may be taken with a light meal, such as dry toast or cornflakes with skim or nonfat milk. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about what foods may be taken with indinavir.
Continue to take indinavir even if you feel well. Do not stop taking indinavir without talking to your doctor.
Your doctor may need to interrupt your treatment if you experience certain side effects. Be sure to tell your doctor how you are feeling during your treatment with indinavir.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor for a copy of the manufacturer's information for the patient.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking indinavir,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to indinavir, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in indinavir capsules. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medications: alfuzosin (Uroxatral); alprazolam (Xanax); amiodarone (Cordarone, Nexterone, Pacerone); cisapride (Propulsid) (not available in the U.S.); ergot-type medications such as dihydroergotamine (D.H.E. 45, Migranal), ergonovine (Ergotrate), ergotamine (Ergomar, in Cafergot, in Migergot), and methylergonovine (Methergine); lovastatin (Altoprev, Mevacor, in Advicor); midazolam (Versed) by mouth; pimozide (Orap); sildenafil (only Revatio brand used for lung disease); simvastatin (Zocor, in Simcor, in Vytorin); or triazolam (Halcion). Your doctor will probably tell you not to take indinavir.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what other prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: bosentan (Tracleer); calcium-channel blockers such as amlodipine (Norvasc, in Amturnide, in Tekamlo), felodipine (Plendil), nicardipine (Cardene), and nifedipine (Adalat, Afeditab, Procardia); carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol, others); cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) such as atorvastatin (Lipitor, in Caduet, in Liptruzet) and rosuvastatin (Crestor); clarithromycin (Biaxin, in PrevPac); colchicine (Colcrys, Mitigare); dexamethasone; fluticasone (Flonase, Flovent, in Advair); itraconazole (Onmel, Sporanox); ketoconazole (Nizoral); other medications for HIV including atazanavir (Reyataz, in Evotaz), delavirdine (Rescriptor), efavirenz (Sustiva, in Atripla), nelfinavir (Viracept), nevirapine (Viramune), ritonavir (Norvir, in Kaletra, in Viekira Pak), and saquinavir (Invirase); medications for irregular heartbeat such as lidocaine (Glydo, Xylocaine) and quinidine (in Nuedexta); medications that suppress the immune system such as cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), sirolimus (Rapamune, Torisel), and tacrolimus (Astagraf XL, Prograf); midazolam (Versed) by injection; certain phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE-5 inhibitors) used for erectile dysfunction such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra, in Staxyn); phenobarbital; phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek, others); quetiapine (Seroquel); rifabutin (Mycobutin); rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane, in Rifamate, in Rifater); salmeterol (Serevent, in Advair); trazodone; and venlafaxine (Effexor). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects. Many other medications may also interact with indinavir, so be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, even those that do not appear on this list.
- tell your doctor what herbal products you are taking, especially St. John's wort.
- if you are taking didanosine (Videx), take it at least one hour before or after indinavir.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had hemophilia (bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly), diabetes, or kidney or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking indinavir, call your doctor. You should not breast-feed if you are infected with HIV or if you are taking indinavir.
- you should know that your body fat may increase or move to different areas of your body such as your breasts, upper back, neck, chest, and stomach area. Loss of fat from the legs, arms, and face can also happen.
- you should know that you may experience hyperglycemia (increases in your blood sugar) while you are taking this medication, even if you do not already have diabetes. Tell your doctor immediately if you have any of the following symptoms while you are taking indinavir: extreme thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, blurred vision, or weakness. It is very important to call your doctor as soon as you have any of these symptoms, because high blood sugar that is not treated can cause a serious condition called ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis may become life-threatening if it is not treated at an early stage. Symptoms of ketoacidosis include: dry mouth, nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, breath that smells fruity, and decreased consciousness.
- you should know that while you are taking medications to treat HIV infection, your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight other infections that were already in your body. This may cause you to develop symptoms of those infections. If you have new or worsening symptoms at anytime during your treatment with indinavir, be sure to tell your doctor.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Indinavir may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if this symptom is severe or does not go away:- change in sense of taste
- rash
- hives
- itching
- peeling or blistering skin
- back pain
- pain in the side of your body
- middle to lower stomach pain
- blood in urine
- muscle pain or weakness
- nausea
- excessive tiredness
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- loss of appetite
- pain in the upper right part of your stomach
- flu-like symptoms
- dark yellow or brown urine
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- shortness of breath
- fast heartbeat
- confusion
- dizziness
- headache
- paleness
Indinavir may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. A desiccant (drying agent) is included with your capsules; keep this in your medicine bottle at all times. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Protease Inhibitors
- Direct Acting Antivirals
- Antivirals for Systemic Use
- Antiinfectives for Systemic Use
- HIV Protease Inhibitors
- CYP2D6 Inducers
- CYP2D6 Inducers (strong)
- Combined Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C19 Inducers
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Protease inhibitors
| Prescribed | Indinavir is an antiretroviral drug for the treatment of HIV infection. |
| Weight : | 613.7895 |
| Structure | Indinavir |
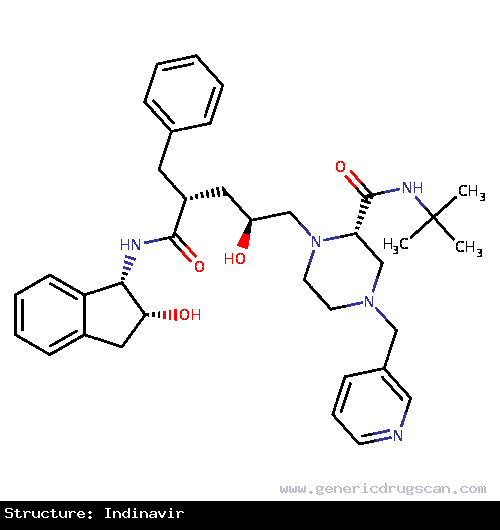 | |
| Formula | C36H47N5O4 |
Indinavir has 7 Brands listed
| I VIR (400 mg) | Inbec (400 mg) |
| Ind (400 mg) | Indease (400 mg) |
| Indivan (400 mg) | Indivir (400 mg) |
| Virodin (400 mg) |
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
