Erlotinib Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Erlotinib
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (er loe' ti nib)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Erlotinib is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or to other parts of the body in patients who have already been treated with at least one other chemotherapy medication and have not gotten better. Erlotinib is also used in combination with another medication (gemcitabine
- Gemzar
How should this medicine be used?
Erlotinib comes as a tablet to take by mouth. It is usually taken on an empty stomach once a day, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating a meal or snack. Take erlotinib at around the same time every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take erlotinib exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor may decrease your dose of erlotinib during your treatment. This depends on how well the medication works for you and the side effects you experience. Talk to your doctor about how you are feeling during your treatment. Continue to take erlotinib even if you feel well. Do not stop taking erlotinib without talking to your doctor.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking erlotinib,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to erlotinib, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in erlotinib tablets. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: angiogenesis inhibitors such as bevacizumab (Avastin); anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin (Coumadin); certain antifungals such as itraconazole (Sporanox), ketoconazole (Nizoral), and voriconazole (Vfend); carbamazepine (Tegretol); ciprofloxacin (Cipro, Proquin XR); clarithromycin (Biaxin); HIV protease inhibitors such as atazanavir (Reyataz), indinavir (Crixivan), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (Norvir), and saquinavir (Fortovase, Invirase); H2 blockers such as cimetidine (Tagamet), famotidine (Pepcid), nizatidine (Axid), and ranitidine (Zantac); medications for acne such as benzoyl peroxide (in Epiduo, in BenzaClin, in Benzamycin, others); midazolam (Versed): nefazodone; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn); oral steroids such as dexamethasone (Decadron, Dexone), methylprednisolone (Medrol), and prednisone (Deltasone); phenobarbital (Luminal, Solfoton); phenytoin (Dilantin); proton pump inhibitors such as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), omeprazole (Prilosec), pantoprazole (Protonix), and rabeprazole (AcipHex); rifabutin (Mycobutin); rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane); rifapentine; taxane medications for cancer such as docetaxel (Taxotere) and paclitaxel (Abraxane, Taxol); telithromycin (Ketek); and troleandomycin (TAO) (not available in the U.S.). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects. Many other medications may also interact with erlotinib, so be sure to tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, even those that do not appear on this list.
- if you are taking antacids, take them several hours before or several hours after you take erlotinib.
- tell your doctor what herbal products you are taking, especially St. John's wort.
- tell your doctor if you are being treated or have recently been treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy (treatment for cancer that uses waves of high energy particles to kill cancer cells). Also tell your doctor if you have or have ever had lung disease or infection, stomach ulcers, diverticular disease (condition in which abnormal pouches form in the large intestine and may become inflamed), or liver or kidney disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. You should not become pregnant while you are taking erlotinib and for at least 2 weeks after your treatment. Talk to your doctor about birth control methods that you can use during your treatment. If you become pregnant while taking erlotinib, call your doctor immediately. Erlotinib may harm the fetus.
- tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking erlotinib.
- tell your doctor if you use tobacco products. Cigarette smoking may decrease the effectiveness of this medication.
- plan to avoid unnecessary or prolonged exposure to sunlight and to wear a hat, other protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen. Choose a sunscreen that has a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15 and contains zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. Exposure to sunlight increases the risk that you will develop a rash during your treatment with erlotinib.
- you should know that erlotinib may cause rashes and other skin problems. To protect your skin, use a mild alcohol-free moisturizer, wash your skin with mild soap, and remove cosmetics with a mild cleanser.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Erlotinib may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- diarrhea
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- vomiting
- heartburn
- gas
- constipation
- stomach pain
- mouth sores
- weight loss
- extreme tiredness
- headache
- bone or muscle pain
- depression
- anxiety
- numbness, burning, or tingling of the hands or feet
- swelling of the arms, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- darkening of skin
- hair loss
- changes in the appearance of the hair and nails
- rash (may look like acne and may affect the skin on the face, upper chest, or back)
- blistering, peeling, dry, or cracked skin
- itching, tenderness, or burning of the skin
- shortness of breath
- cough
- fever or chills
- growth of eyelashes on the inside of the eyelid
- dry, red, painful, or irritated eyes
- blurred vision
- chest pain or pressure
- pain in the arms, neck, or upper back
- rapid, irregular, or pounding heartbeat
- slow or difficult speech
- dizziness or faintness
- weakness or numbness of an arm or leg
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- black and tarry or bloody stools
- vomit that is bloody or looks like coffee grounds
- sunken eyes
- dry mouth
- decreased urination
- dark urine
- pale or yellow skin
- redness, warmth, pain, tenderness, or swelling in one leg
Erlotinib may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program.
Drug Category/Class
- Protein Kinase Inhibitors
- Antineoplastic Agents
- Antineoplastic and Immunomodulating Agents
- CYP2D6 Inducers
- CYP2D6 Inducers (strong)
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inducers
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Protein kinase inhibitors
| Prescribed | For the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regim... |
| Weight : | 393.4357 |
| Structure | Erlotinib |
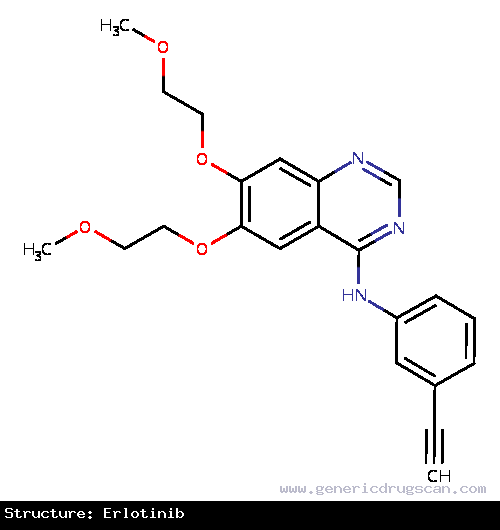 | |
| Formula | C22H23N3O4 |
Erlotinib has 2 Brands listed
| Erlocip (150 mg) | Lortinib (150 mg) |
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
