Diazepam Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Diazepam
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (dye az' e pam)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Diazepam is used to relieve anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizures and to control agitation caused by alcohol withdrawal.
How should this medicine be used?
Diazepam comes as a tablet, extended-release (long-acting) capsule, and concentrate (liquid) to take by mouth. Do not open, chew, or crush the extended-release capsules; swallow them whole. It is usually taken 1 to 4 times a day and may be taken with or without food. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take diazepam exactly as directed.
Diazepam concentrate (liquid) comes with a specially marked dropper for measuring the dose. Ask your pharmacist to show you how to use the dropper. Dilute the concentrate in water, juice, or carbonated beverages just before taking it. It also may be mixed with applesauce or pudding just before taking the dose.
Diazepam can be habit-forming. Do not take a larger dose, take it more often, or for a longer time than your doctor tells you to. Tolerance may develop with long-term or excessive use, making the drug less effective. This medication must be taken regularly to be effective. Do not skip doses even if you feel that you do not need them. Do not take diazepam for more than 4 months or stop taking this medication without talking to your doctor. Stopping the drug suddenly can worsen your condition and cause withdrawal symptoms (anxiousness, sleeplessness, and irritability). Your doctor probably will decrease your dose gradually.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking diazepam,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to diazepam, alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium, Librax), clonazepam (Klonopin), clorazepate (Tranxene), estazolam (ProSom), flurazepam (Dalmane), lorazepam (Ativan), oxazepam (Serax), prazepam (Centrax), temazepam (Restoril), triazolam (Halcion), or any other drugs.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications you are taking, especially antihistamines; cimetidine (Tagamet); digoxin (Lanoxin); disulfiram (Antabuse); fluoxetine (Prozac); isoniazid (INH, Laniazid, Nydrazid); ketoconazole (Nizoral); levodopa (Larodopa, Sinemet); medications for depression, seizures, pain, Parkinson's disease, asthma, colds, or allergies; metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL); muscle relaxants; oral contraceptives; probenecid (Benemid); propoxyphene (Darvon); propranolol (Inderal); ranitidine (Zantac); rifampin (Rifadin); sedatives; sleeping pills; theophylline (Theo-Dur); tranquilizers; valproic acid (Depakene); and vitamins. These medications may add to the drowsiness caused by diazepam.
- if you use antacids, take diazepam first, then wait 1 hour before taking the antacid.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had glaucoma; seizures; or lung, heart, or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking diazepam, call your doctor immediately.
- talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of taking diazepam if you are 65 years of age or older. Older adults should not usually take diazepam because it is not as safe as other medications that can be used to treat the same conditions.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking diazepam.
- you should know that this drug may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this drug affects you.
- remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this drug.
- tell your doctor if you use tobacco products. Cigarette smoking may decrease the effectiveness of this drug.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Side effects from diazepam are common and include the following:- drowsiness
- dizziness
- tiredness
- weakness
- dry mouth
- diarrhea
- nausea
- changes in appetite
- restlessness or excitement
- constipation
- difficulty urinating
- frequent urination
- blurred vision
- changes in sex drive or ability
- seizures
- shuffling walk
- persistent, fine tremor or inability to sit still
- fever
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- severe skin rash
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- irregular heartbeat
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Anti-Anxiety Agents
- Hypnotics and Sedatives
- Anticonvulsants
- Anesthetics, Intravenous
- Adjuvants, Anesthesia
- GABA Modulators
- Muscle Relaxants, Central
- Antiemetics
- Nervous System
- Benzodiazepine Derivatives
- Anxiolytics
- Psycholeptics
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inducers
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C8 Inhibitors
- C
| Prescribed | Used in the treatment of severe anxiety disorders, as a hypnotic in the short-term management of insomnia, as a sedative and premedicant, as an ant... |
| Weight : | 284.74 |
| Structure | Diazepam |
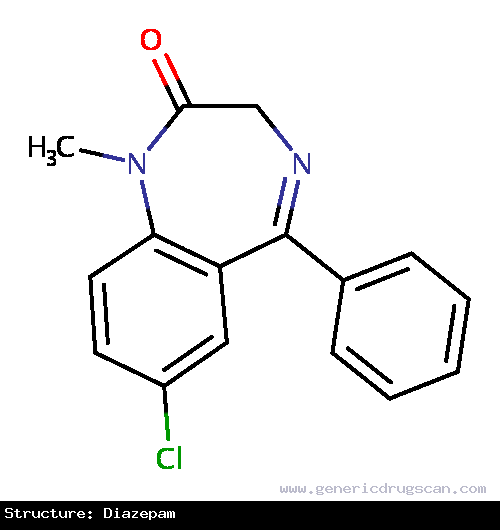 | |
| Formula | C16H13ClN2O |
Diazepam has 90 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
