Clindamycin Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Clindamycin
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (klin'' da mye' sin)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Clindamycin is used to treat certain types of bacterial infections, including infections of the lungs, skin, blood, female reproductive organs, and internal organs. Clindamycin is in a class of medications called lincomycin antibiotics. It works by slowing or stopping the growth of bacteria. Antibiotics such as clindamycin will not kill the viruses that cause colds, flu, and other infections.
How should this medicine be used?
Clindamycin comes as a capsule and a solution (liquid) to take by mouth. It is usually taken three to four times a day. The length of your treatment depends on the type of infection you have. Take clindamycin at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take clindamycin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Shake the liquid well before each use to mix the medication evenly.
Take the capsules with a full glass of water so that the medication will not irritate your throat.
You should begin to feel better during the first few days of treatment with clindamycin. If your symptoms do not improve or if they get worse, call your doctor.
Take clindamycin until you finish the prescription, even if you feel better. If you stop taking clindamycin too soon or skip doses, your infection may not be completely treated and the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking clindamycin,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to clindamycin, lincomycin (Lincocin), or any other medications. If you will be taking clindamycin capsules, tell your doctor if you are allergic to aspirin or tartrazine (a yellow dye found in some medications).
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention erythromycin (E.E.S, E-Mycin, Erythrocin, others). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had asthma, allergies, eczema (sensitive skin that often becomes itchy or irritated) or kidney or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking clindamycin, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking clindamycin.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Clindamycin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- nausea
- vomiting
- joint pain
- pain when swallowing
- heartburn
- white patches in the mouth
- thick, white vaginal discharge
- burning, itching, and swelling of the vagina
- blisters
- rash
- hives
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- decreased urination
Clindamycin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Do not refrigerate clindamycin liquid because it may thicken and become hard to pour. Throw away any unused clindamycin solution after 2 weeks. Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
- Anti-Acne Preparations
- Anti-Acne Preparations for Topical Use
- Antiinfectives for Treatment of Acne
- Macrolides, Lincosamides and Streptogramins
- Lincosamides
- Dermatologicals
- Gynecological Antiinfectives and Antiseptics
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Anti-Bacterial Agents
- Antibiotics
- Genito Urinary System and Sex Hormones
- Antibacterials for Systemic Use
- Antii
| Prescribed | For the treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria, including Bacteroides spp., Peptostreptococcus, anaerobic strepto... |
| Weight : | 424.983 |
| Structure | Clindamycin |
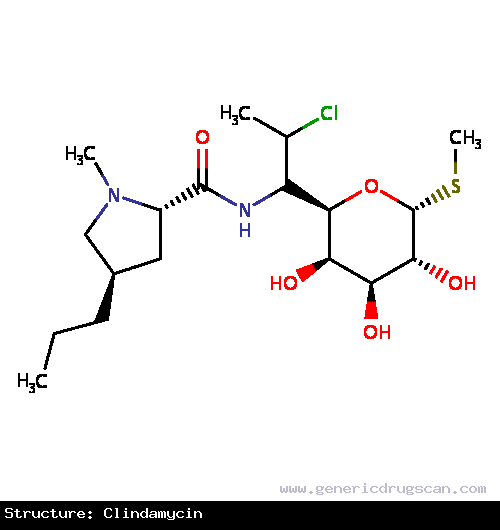 | |
| Formula | C18H33ClN2O5S |
Clindamycin has 95 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
