Bupropion Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Bupropion
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (byoo proe' pee on)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Bupropion (Aplenzin, Wellbutrin, Wellbutrin SR, Wellbutrin XL) is used to treat depression. Bupropion (Aplenzin, Wellbutrin XL) is also used to treat seasonal affective disorder (SAD; episodes of depression that occur at the same time each year
- usually in the fall and winter but rarely may occur in the spring or summer months
How should this medicine be used?
Bupropion comes as a tablet and a sustained-release or extended-release (long-acting) tablet to take by mouth. The regular tablet (Wellbutrin) is usually taken three times a day, with doses at least 6 hours apart, or four times a day, with doses at least 4 hours apart. The sustained-release tablet (Wellbutrin SR, Zyban) is usually taken twice a day, with doses at least 8 hours apart. The extended-release tablet (Aplenzin, Wellbutrin XL) is usually taken once daily in the morning; doses of the extended-release tablet should be taken at least 24 hours apart. When bupropion is used to treat seasonal affective disorder, it is usually taken once a day in the morning beginning in the early fall, continuing through the winter, and stopping in the early spring. Sometimes a lower dose of bupropion is taken for 2 weeks before the medication is stopped. Take bupropion with food if the medication upsets your stomach. If you have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, do not take bupropion too close to bedtime. Take bupropion at around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take bupropion exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the sustained-release and extended-release tablets whole; do not split, chew, or crush them.
Your doctor will probably start you on a low dose of bupropion and gradually increase your dose.
It may take 4 weeks or longer before you feel the full benefit of bupropion. Continue to take bupropion even if you feel well. Do not stop taking bupropion without talking to your doctor. Your doctor may decrease your dose gradually.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking bupropion,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to bupropion, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in bupropion tablets. Ask your pharmacist or check the Medication Guide for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor if you are taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), linezolid (Zyvox), methylene blue, phenelzine (Nardil), selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam, Zelapar), and tranylcypromine (Parnate), or if you have stopped taking an MAO inhibitor within the past 14 days. Your doctor will probably tell you not to take bupropion.
- do not take more than one product containing bupropion at a time. You could receive too much medication and experience severe side effects.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what other prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: amantadine (Symmetrel); beta blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), labetalol (Normodyne), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL), nadolol (Corgard), and propranolol (Inderal); cimetidine (Tagamet); clopidogrel (Plavix); cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan, Neosar); efavirenz (Sustiva, in Atripla); insulin or oral medications for diabetes; medications for irregular heartbeat such as flecainide (Tambocor) and propafenone (Rythmol); medications for mental illness such as haloperidol (Haldol), risperidone (Risperdal), and thioridazine (Mellaril); medications for seizures such as carbamazepine (Tegretol), phenobarbital (Luminal, Solfoton), and phenytoin (Dilantin); levodopa (Sinemet, Larodopa); lopinavir and ritonavir (Kaletra); nelfinavir (Viracept); nicotine patch; oral steroids such as dexamethasone (Decadron, Dexone), methylprednisolone (Medrol), and prednisone (Deltasone); orphenadrine (Norflex); other antidepressants such as citalopram (Celexa), desipramine (Norpramin), fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem, in Symbyax), fluvoxamine (Luvox), imipramine (Tofranil), nortriptyline (Aventyl, Pamelor), paroxetine (Paxil) and sertraline (Zoloft); ritonavir (Norvir); sedatives; sleeping pills; tamoxifen (Nolvadex, Soltamox); theophylline (Theobid, Theo-Dur, others); thiotepa; and ticlopidine (Ticlid). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had seizures, anorexia nervosa (an eating disorder) or bulimia (an eating disorder). Also tell your doctor if you drink large amounts of alcohol but expect to suddenly stop drinking or you take sedatives but expect to suddenly stop taking them. Your doctor will probably tell you not to take bupropion.
- tell your doctor if you drink large amounts of alcohol, use street drugs, or overuse prescription medications and if you have ever had a heart attack; a head injury; a tumor in your brain or spine; high blood pressure; diabetes; or liver, kidney, or heart disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking bupropion, call your doctor.
- you should know that bupropion may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this medication affects you.
- talk to your doctor about the safe use of alcoholic beverages while you are taking bupropion. Alcohol can make the side effects from bupropion worse.
- you should know that bupropion may cause an increase in your blood pressure. Your doctor may check your blood pressure before starting treatment and regularly while you are taking this medication, especially if you also are using nicotine replacement therapy.
- you should know that bupropion may cause angle-closure glaucoma (a condition where the fluid is suddenly blocked and unable to flow out of the eye causing a quick, severe increase in eye pressure which may lead to a loss of vision). Talk to your doctor about having an eye examination before you start taking this medication. If you have nausea, eye pain, changes in vision, such as seeing colored rings around lights, and swelling or redness in or around the eye, call your doctor or get emergency medical treatment right away.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Bupropion may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:- drowsiness
- anxiety
- excitement
- difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- dry mouth
- dizziness
- headache
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- uncontrollable shaking of a part of the body
- loss of appetite
- weight loss
- constipation
- excessive sweating
- ringing in the ears
- changes in your sense of taste
- frequent urination
- sore throat
- seizures
- confusion
- hallucinating (seeing things or hearing voices that do not exist)
- irrational fears
- muscle or joint pain
- rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
- fever
- rash or blisters
- itching
- hives
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- hoarseness
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- chest pain
Bupropion may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from light, excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Throw away any medication that is outdated or no longer needed. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
Drug Category/Class
- Antidepressive Agents, Second-Generation
- Dopamine Uptake Inhibitors
- Antidepressants
- Psychoanaleptics
- Centrally Acting Antiobesity Products
- Antiobesity Preparations, Excl. Diet Products
- CYP2D6 Inducers
- CYP2D6 Inducers (strong)
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inducers
- Alimentary Tract and Metabolism
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C9 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-45
| Prescribed | For the treatment of depression and as aid to smoking cessation. |
| Weight : | 239.741 |
| Structure | Bupropion |
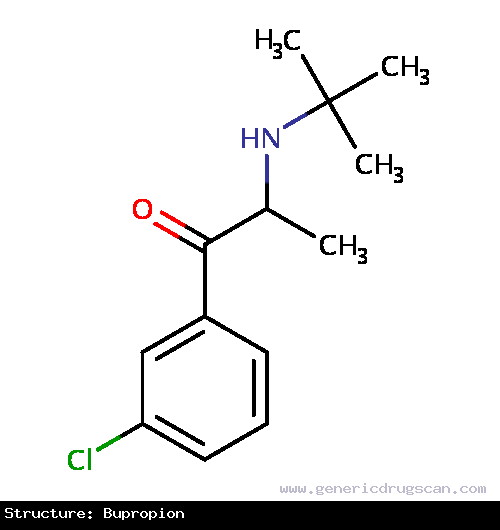 | |
| Formula | C13H18ClNO |
Bupropion has 13 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
