Aminophylline Drug: Indication, Dosage, Precaution, Side Effect , Storage, Category Type and corresponding Brands - www.genericdrugscan.com
Aminophylline
Drug Status in USA : ApprovedDrug Status in Canada : Approved
pronunciation
pronounced as (am in off'' i lin)
Why is this medication prescribed?
Aminophylline is used to prevent and treat wheezing, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing caused by asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung diseases. It relaxes and opens air passages in the lungs, making it easier to breathe.
This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should this medicine be used?
Aminophylline comes as a tablet and syrup to take by mouth and a suppository to insert rectally. It usually is taken every 6, 8, or 12 hours. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take aminophylline exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Take the tablets or oral liquid with a full glass of water on an empty stomach, at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. Do not chew or crush the long-acting tablets; swallow them whole.
Aminophylline controls symptoms of asthma and other lung diseases but does not cure them. Continue to take aminophylline even if you feel well. Do not stop taking aminophylline without talking to your doctor.
To insert a rectal suppository, follow these steps:Remove the wrapper.Dip the tip of the suppository in water.Lie down on your left side and raise your right knee to your chest. (A left-handed person should lie on the right side and raise the left knee.)Using your finger, insert the suppository into the rectum, about 1/2 to 1 inch (1.25 to 2.5 centimeters) in infants and children and 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in adults. Hold it in place for a few moments.Stand up after about 15 minutes. Wash your hands thoroughly and resume your normal activities.
What are the precautions to be followed?
Before taking aminophylline,- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to aminophylline or any other drugs.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription medications you are taking, especially allopurinol (Zyloprim), azithromycin (Zithromax) carbamazepine (Tegretol), cimetidine (Tagamet), ciprofloxacin (Cipro), clarithromycin (Biaxin), diuretics ('water pills'), erythromycin, lithium (Eskalith, Lithobid), oral contraceptives, phenytoin (Dilantin), prednisone (Deltasone), propranolol (Inderal), rifampin (Rifadin), tetracycline (Sumycin), and other medications for infections or heart disease.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what nonprescription medications and vitamins you are taking, especially nonprescription medications containing ephedrine, epinephrine, phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, or pseudoephedrine. Many nonprescription products contain these drugs (e.g., diet pills and medications for colds and asthma), so check labels carefully. Do not take these medications without talking to your doctor; they can increase the side effects of aminophylline.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had seizures, heart disease, an overactive or underactive thyroid gland, high blood pressure, or liver disease or if you have a history of alcohol abuse.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking aminophylline, call your doctor.
- tell your doctor if you use tobacco products. Cigarette smoking may affect the effectiveness of aminophylline.
What are possible side effects of this medication ?
Aminophylline may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away.- upset stomach
- stomach pain
- diarrhea
- headache
- restlessness
- insomnia
- irritability
- vomiting
- increased or rapid heart rate
- irregular heartbeat
- seizures
- skin rash
How to store the medication and dispose it of after its use later?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom).
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program.
Drug Category/Class
- Purinergic P1 Receptor Antagonists
- Bronchodilator Agents
- Muscle Relaxants, Respiratory
- Xanthines
- Xanthines and Adrenergics
- CYP2E1 Inhibitors
- CYP2E1 Inducers
- CYP2E1 Inducers (strong)
- Respiratory System
- Drugs for Obstructive Airway Diseases
- Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
- Cardiotonic Agents
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inducers
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
| Prescribed | For the treatment of bronchospasm due to asthma, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. |
| Weight : | 420.4264 |
| Structure | Aminophylline |
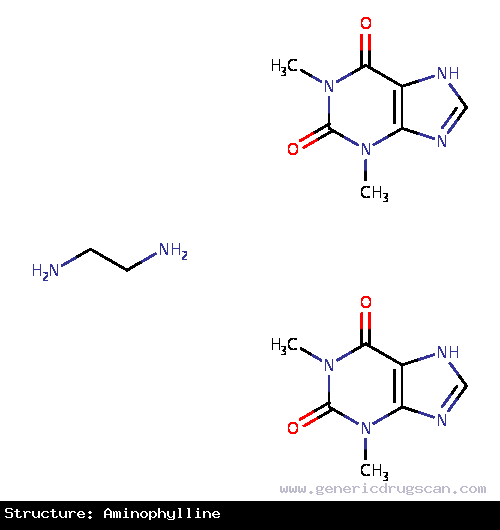 | |
| Formula | C16H24N10O4 |
Aminophylline has 9 Brands listed
Search Generic Drugs alphabetically
